Inflammation and aging are closely linked, and not in a good way. While short-term inflammation helps you heal, chronic inflammation speeds up cell damage, weakens your immune system, and raises your biological age.
The good news? It’s fixable. This guide shows how to spot it, what science says, and how to reduce inflammation to age better.
Table of Contents
What Is Chronic Inflammation and Why Does It Matter for Aging?
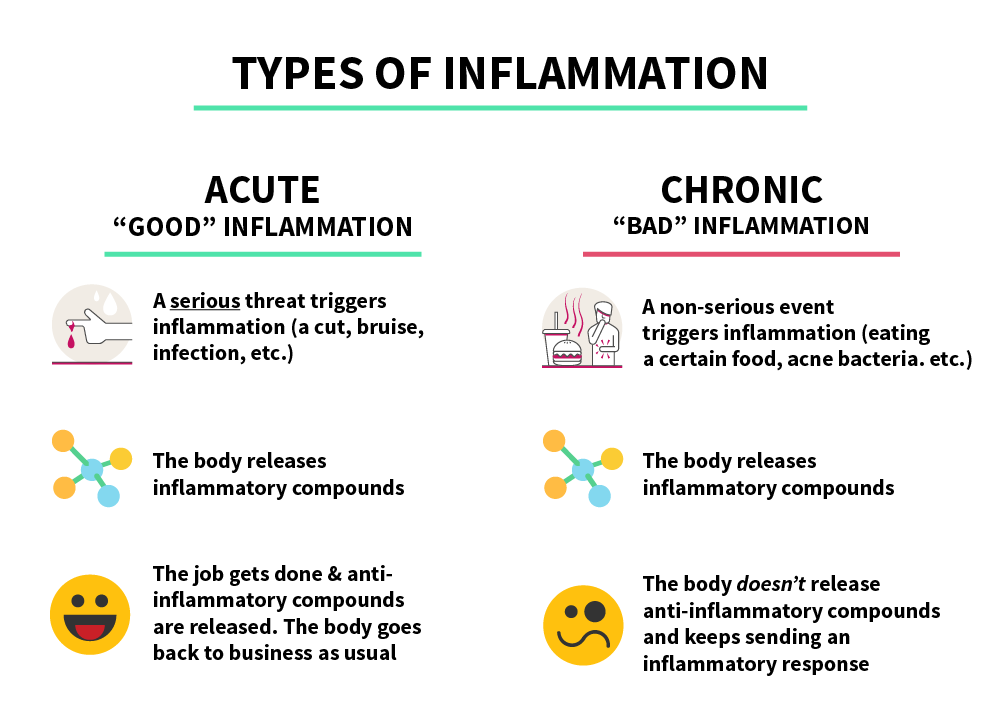
🔥 When you get a cut or an infection, your body launches a short-term immune response. That’s acute inflammation, and it’s useful. But when the immune system stays slightly “on” all the time, that’s chronic inflammation, and it’s harmful. Over time, this low-level fire damages your blood vessels, tissues, and even your DNA.
According to researchers from Columbia University’s public health school, chronic inflammation is not a universal feature of aging but often reflects lifestyle, infection load, and environment. In populations with low lifetime infections and better diets, age-related inflammation is surprisingly lower (Columbia University).
How Does Inflammation Speed Up Biological Aging?
🧠 Chronic inflammation increases oxidative stress, telomere shortening, and epigenetic drift, the cellular hallmarks of aging. It affects:
- Mitochondria (energy decline)
- Hormone balance (especially cortisol, insulin, and estrogen/testosterone)
- Brain function (linked to Alzheimer’s)
- Immune system fatigue (immunosenescence)
A study published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy in 2023 describes inflammation as both a trigger and amplifier of aging-related disease, especially cardiovascular and metabolic disorders (Nature).
How Do You Know If You Have Inflammation?
🧪 There’s no perfect at-home test, but signs of chronic inflammation may include:
- Fatigue or brain fog
- Frequent infections or slow healing
- Joint or muscle aches without clear injury
- Puffy face or eyes
- Skin conditions (like eczema, acne, or rosacea)
- Digestive issues (bloating, cramps, IBS)
For a more accurate view, some blood tests like CRP, IL-6, or TNF-alpha are used by longevity doctors. But your biological age score may also reflect inflammation levels over time. You can compare leading at-home testing kits here: Biological Age Test Kit Comparison
Can Inflammation Predict Cognitive Decline and Longevity?
🧠 Yes. According to a 2024 study on aging-related neuroinflammation in PubMed Central, elevated inflammatory markers were strongly associated with reduced memory and increased risk of neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s (PubMed).
Experts like Dr. Ronald Klatz, a leader in the anti-aging medicine field, emphasize the need to control inflammation early, not just when symptoms show. Learn more from his work here: Dr. Ronald Klatz on Longevity
What Lifestyle Changes Lower Inflammation Naturally?
🥗 You don’t need extreme interventions. Small, consistent changes work best.
✅ Anti-Inflammatory Habits That Work:
- Eat omega-3 fats: found in fish, flaxseed, and walnuts.
- Limit processed sugar and seed oils.
- Move daily: Walking, strength training, or stretching.
- Improve sleep quality: Aim for 7–9 hours of uninterrupted rest.
- Meditation or breathwork: Lowers cortisol and IL-6 markers.
- Spices like turmeric and ginger show natural anti-inflammatory effects.
Dr. Barry Sears, known for the Zone Diet and decades of research on eicosanoids and inflammation, suggests that food can be your most powerful anti-aging tool. You can explore his full approach here: Dr. Barry Sears on Inflammation & Diet
What About “Weird” Therapies Like Hirudotherapy and Bee Venom?
Some of the strangest-sounding therapies might hold real anti-inflammatory power, and many of them have roots in traditional medicine and are under active scientific review.
🩸 Hirudotherapy (Leech Therapy)
Used for centuries, medical leech therapy is still practiced today in hospitals across Europe and the U.S., especially for reconstructive surgeries and blood circulation problems. The secret? Leech saliva contains more than 20 bioactive compounds that:
- Thin the blood
- Reduce local inflammation
- Improve microcirculation
- Deliver natural anesthetics and vasodilators
Recent studies show potential use of hirudotherapy for arthritis, varicose veins, and chronic inflammatory skin conditions. It may sound medieval, but it’s FDA-approved for specific procedures. Want to explore the research behind it? Start here: Hirudotherapy in Modern Medicine
🐝 Apitherapy (Bee Venom Therapy)
Yes, bee stings. While obviously not for the allergic or faint-hearted, apitherapy uses controlled doses of bee venom (or purified melittin) to treat inflammatory conditions. Research shows bee venom may:
- Reduce inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis
- Modulate immune responses
- Suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6
- Stimulate cortisol release from the adrenal glands
While still considered experimental in the West, apitherapy is used in Korea, Eastern Europe, and parts of South America with formal training programs. It’s not DIY, medical supervision is critical.
🧫 Helminthic Therapy (Yes, Worms)
This might be the wildest of them all: helminthic therapy involves introducing controlled, non-replicating intestinal parasites (like Necator americanus or Trichuris suis) to regulate an overactive immune system.
Why would anyone do this?
Because some autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, like Crohn’s, multiple sclerosis, and even allergies, are linked to hyperactive immunity. These organisms evolved to calm inflammation so they could survive inside us. That calming effect may benefit humans, too.
Emerging studies and pilot trials show promise, especially for:
- IBD (inflammatory bowel disease)
- Autoimmune arthritis
- Chronic allergic inflammation
This therapy is highly controversial and still experimental, but it’s part of a growing movement to explore evolutionary medicine and how our microbiome (and ancient parasites) influence systemic inflammation.
What’s the Role of Epigenetics and Inflammation?
🧬 Epigenetic clocks (like DunedinPACE or Horvath’s Clock) measure how your lifestyle and inflammation are impacting your DNA regulation. Unlike genetic tests, these change with your habits.
In short: reducing inflammation today can slow your biological aging next month.
Biohackers are now using this concept to test what works: from diet shifts to NAD+ support, cold exposure, and smart supplements. You can find ideas and tools on our partner site: Daily Biohacking – Start Here
Can You Reverse the Damage Caused by Inflammation?
🧠 You can’t erase every effect of years of chronic inflammation, but you can slow or stop the progression.
Some of the most promising strategies include:
- Testing your baseline biological age and inflammation status
- Using cold therapy (cryotherapy, cold plunges) to train your immune system
- Short fasting windows (12–16h) to reduce inflammatory markers
- Prioritizing sleep, especially deep sleep cycles for cellular repair
- Regular low-intensity movement (walking, gardening, house chores)
Experts from Harvard’s School of Public Health emphasize that while acute inflammation is necessary, long-term control of chronic inflammation may be the key to preventing nearly all age-related diseases (Harvard).
Want to Go Deeper?
📺 We highly recommend this expert-led panel on inflammation and aging hosted by Harvard Chan Studio:
FAQs
What’s the difference between silent inflammation and regular inflammation?
Silent inflammation refers to low-level, ongoing immune activation that doesn’t cause pain or redness, but still damages tissues and accelerates aging. Unlike acute inflammation (like a sore throat or swollen ankle), silent inflammation works in the background, increasing your risk of heart disease, dementia, and even accelerated biological aging. It’s often linked to poor diet, chronic stress, and poor sleep.
Can tracking HRV (heart rate variability) help measure inflammation and aging?
Yes. While HRV isn’t a direct test for inflammation, low HRV is a strong sign your nervous system is under stress, often tied to chronic inflammation and poor recovery. Biohackers use HRV as a daily marker of systemic balance. Improving HRV through sleep, breathwork, and cold exposure may reflect reduced inflammatory burden over time.
Does biological age testing show the impact of inflammation from stress or poor sleep?
Absolutely. Many epigenetic tests, like DunedinPACE or GlycanAge, pick up changes triggered by poor sleep, cortisol imbalances, and even emotional stress. These factors directly influence your immune and metabolic age, so if you improve your lifestyle, your biological age score may drop, sometimes in just a few months.
What herbs are proven to lower inflammation without side effects?
Some of the most studied anti-inflammatory herbs include curcumin (turmeric extract), boswellia, ginger, and ashwagandha. These may reduce levels of CRP and IL-6 in mild chronic inflammation. They’re often used in traditional systems like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine, and have shown promise in clinical trials with fewer side effects than NSAIDs.
Is there a connection between gut inflammation and skin aging?
Yes. The gut-skin axis links intestinal inflammation to skin conditions like eczema, rosacea, and accelerated skin aging. A leaky gut or dysbiosis can trigger systemic inflammation, which may affect collagen breakdown and oxidative stress in the skin. Balancing your microbiome with diet and probiotics may improve both gut and skin health.
How does bee venom therapy reduce inflammation if it’s a toxin?
It sounds contradictory, but bee venom (especially melittin) triggers a mild immune response that can reset overactive inflammation. In low, controlled doses, it modulates cytokine production and may block inflammatory enzymes like COX-2. The goal isn’t to “kill inflammation,” but to retrain the immune system in conditions like arthritis or autoimmune disease.
Created by SimplyAntiAging.com’s Editorial Research Team
Reviewed and updated for accuracy in January 2026.